new Neuron(options)
Neurons are the engines that process and guide information though a neural network. A neural networks "intelligence" is usually measured by the ability for neurons to effectively process information as a group.
What is a neuron?
A Neuron is a simplified mathematical model of a biological neuron.
In people, a neuron is a cell that collects inputs from synapses (i.e. eyes,
ears, etc. or other neurons) and triggers an output signal when the
incoming signals pass a certain threshold.
In biological neurons (in animals) or in artificial neurons (i.e. AI, NN, Deep Learning, etc.), one neuron doesn’t do much, but when combined, neural networks allow us to recognize the world around us, solve problems, and interact with our environment.
How do they work?
Neural networks were inspired by the human brain, and like in a human brain
the basic building block is called a Neuron. Its functionality is similar
to a human neuron, i.e. it takes in some inputs and fires an output. In
purely mathematical terms, a neuron in the machine learning world is a
placeholder for a mathematical function, and its only job is to provide an
output by applying the function on the inputs provided.
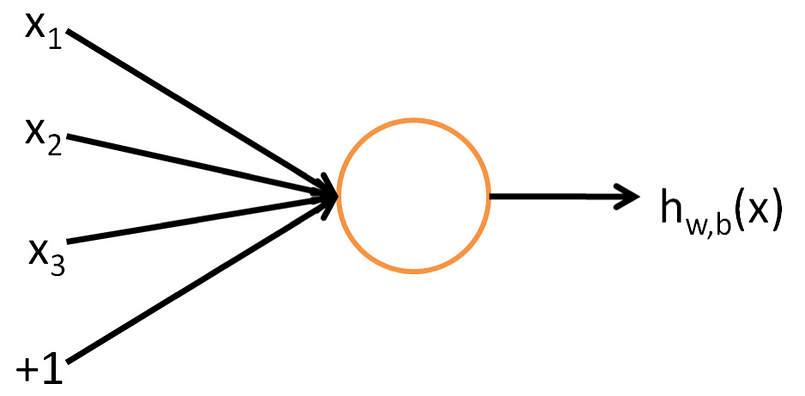
The function used in a neuron is generally called an "activation function". There have been 5 major activation functions tried to date, step, sigmoid, tanh, and ReLU. For this neuron we are using a "sigmoid" activation function.
What is a "sigmoid activation function"?
A sigmoid function - or logistic function - is defined mathematically as:

The value of the function tends to zero when z tends to negative infinity and tends to 1 when z tends to infinity. A sigmoid activation function is an approximation of how a "real neuron" would behave; it's an assumption in the field of deep learning.
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
options |
Object |
Properties
|
Properties:
| Name | Type | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
id |
string | ||||||||||||||||||||||
bias |
number | ||||||||||||||||||||||
optimizer |
Object |
Properties
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
incoming |
Object |
Properties
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
outgoing |
Object |
Properties
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
_output |
number | ||||||||||||||||||||||
output |
number | ||||||||||||||||||||||
error |
number |
Example
//===============================================
// One Neuron (No Hidden Layers) ================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
neuron.activate(0); // 0
neuron.propagate(1); // -1
//===============================================
// Three Neurons (Hidden Layers) ================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const input = new Neuron(); // Input Neuron (Layer)
const hidden = new Neuron(0.1); // Hidden Neuron (Layer)
const output = new Neuron(0.2); // Output Neuron (Layer)
input.connect(hidden, 0.3); // Connects input layer to hidden layer
hidden.connect(output, 0.4); // Connects hidden layer to output layer
input.activate(0); // 0
hidden.activate(); // 0.52497918747894
output.activate(); // 0.6010858826658407
output.propagate(1); // -0.09565228299910712
hidden.propagate(); // -0.009900697661026392
input.propagate(); // -0.0029702092983079176Members
(static) optimizers
Optimizers are initiated with { rate, momentum, decay, alpha, beta, epsilon, gamma }
Methods
activate(inputopt) → {number}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
number |
<optional> |
Returns:
Returns the neuron's output
- Type
- number
Example
//===============================================
// One Neuron ===================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
neuron.activate(3);
//===============================================
// Two Neurons ==================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
const other = new Neuron(0.1);
neuron.connect(other, 0.2);
neuron.activate(3); // 3
other.activate(); // 0.6681877721681662connect(neuron, weightopt)
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
neuron |
Neuron | ||
weight |
number |
<optional> |
Example
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
const other = new Neuron();
neuron.connect(other);propagate(target, rateopt) → {number}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
target |
number | |||
rate |
number |
<optional> |
0.3 |
Returns:
Returns neuron's marginal error
- Type
- number
Example
//===============================================
// One Neuron ===================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
neuron.activate(3); // 3
neuron.propagate(0); // 3
//===============================================
// Two Neurons ==================================
//===============================================
const { Neuron } = require("@liquidcarrot/nn")
const neuron = new Neuron();
const other = new Neuron(0.1);
neuron.connect(other, 0.2);
neuron.activate(3); // 3
other.activate(); // 0.6681877721681662
other.propagate(0); // 0.14814583086672545
neuron.propagate(); // 0.009876697690471913weights(arrayopt) → {Object|Array.<Array.<Number>>}
Parameters:
| Name | Type | Attributes | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
array |
boolean |
<optional> |
false | Iff |
Returns:
Returns an Array or Object of incoming and outgoing weights
- Type
- Object | Array.<Array.<Number>>